Computer simulator “Detection and killing of gas, water or oil kicks” is designated to train personnel to be ready to correctly kill the gas, water and oil kicks at wells and to train their skills according to standard action plan of localization and liquidation of accidents.
Software package of the simulator makes the task implementation process fully automated providing training to any number of trainees. This goal is attained by:
- using the automated system of knowledge control (ASKC) “Razvitie” that provides centralized work of teachers and trainees at their working places (WP) with problem solving and getting results;
- providing automated adaptive scale control for “slow” processes (pumping fluid, solution preparation, etc.) while performing tasks;
- providing automated final evaluation of tasks by the scale from 0 to 100 on the basis of penalty criteria with detail report for the teacher.
The simulator provides both collective and individual tasks. A teacher can select any learning mode from three available: demonstration, training, examination.
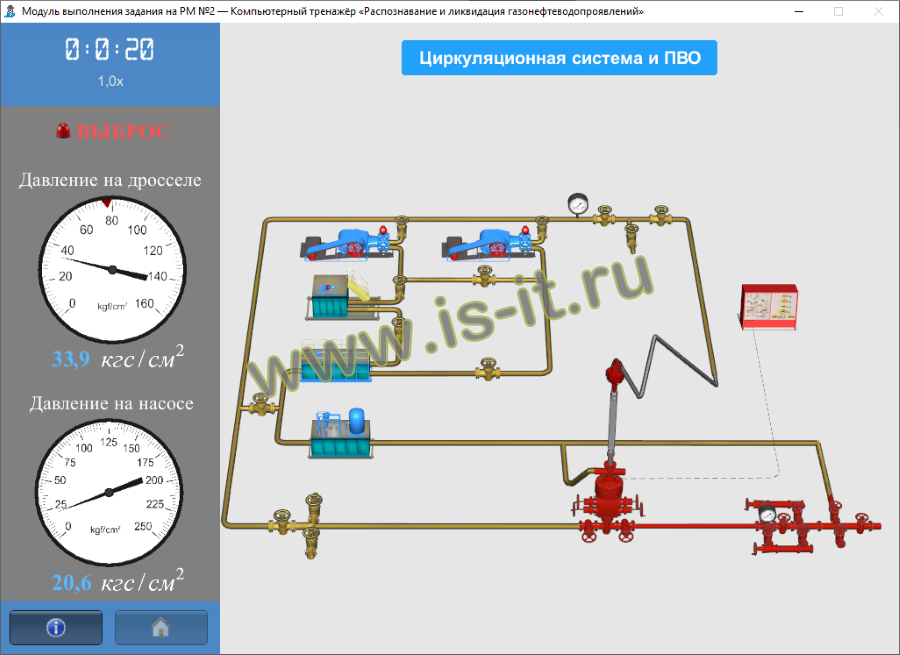
To implement tasks, trainees form working groups of two: a driller and a driller's assistant. A teacher connects to the working group and follows the their actions as well as the well and equipment parameters (well column, base pressure, working operations, operation log, etc.) The simulator features the following types of collective tasks:
- well shut-in after detecting the kick while drilling,
- well shut-in after detecting the kick when lifting the oil-well tubing during well servicing,
- driller's method,
- wait and weight method.
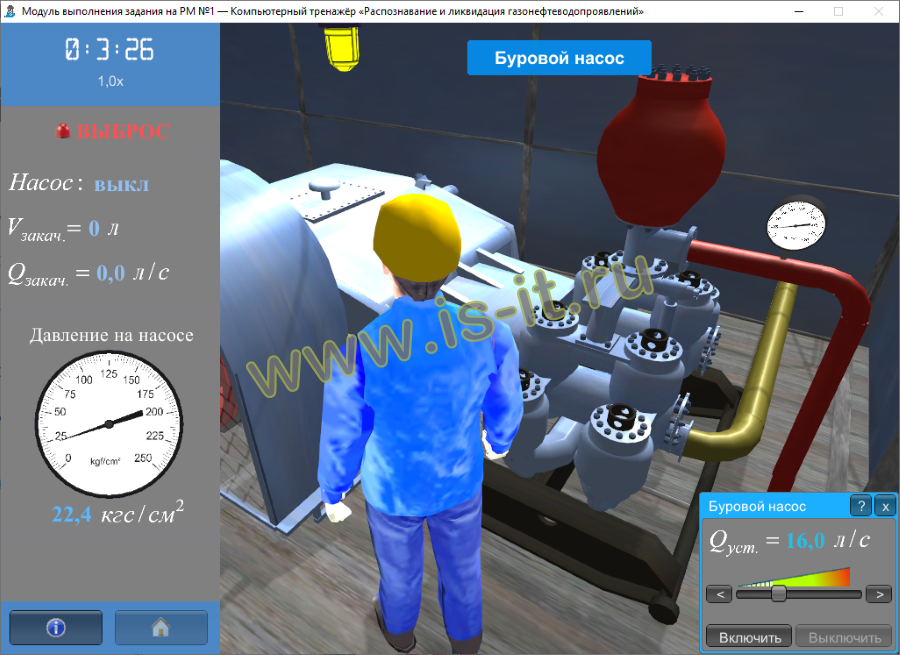
The individual task is implemented by a trainee at his own WP. Learners train their skills acting as drillers or as the first, second and third assistant drillers. The simulator features the following individual tasks:
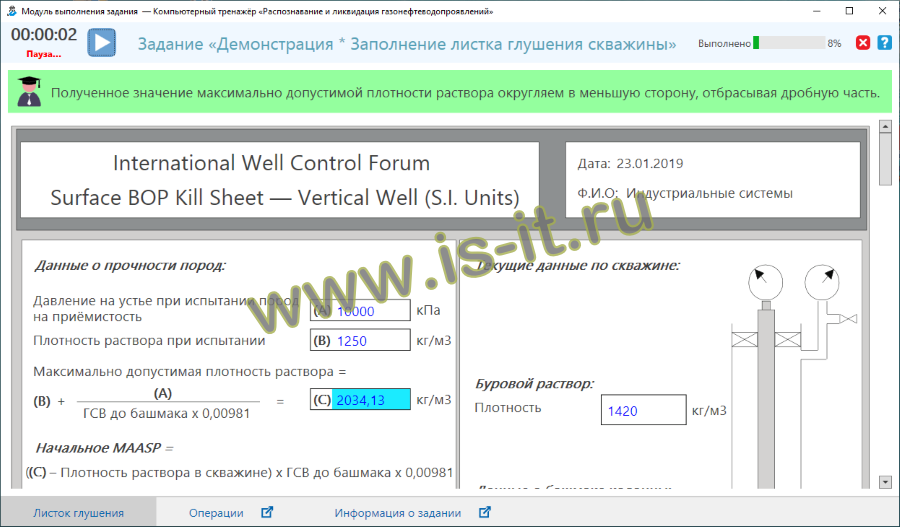
- filling out kill sheet (IWCF, russian version);
- driller's method;
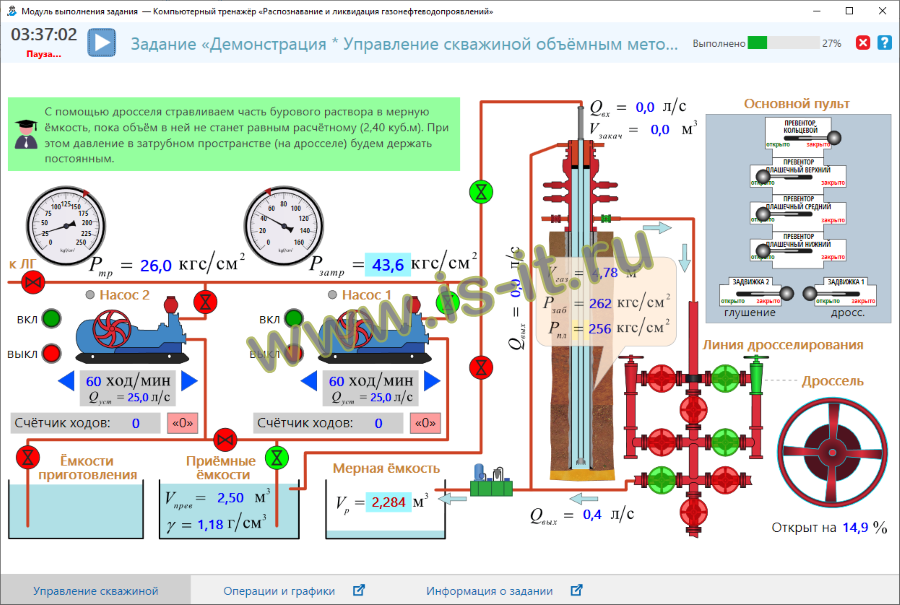
- volumetric method;
- Individual tasks concerning emergency situations (implications) that may occur during kick killing:
- bit nozzle driving,
- bit nozzle washing,
- choke driving,
- choke washing,
- pump failure;
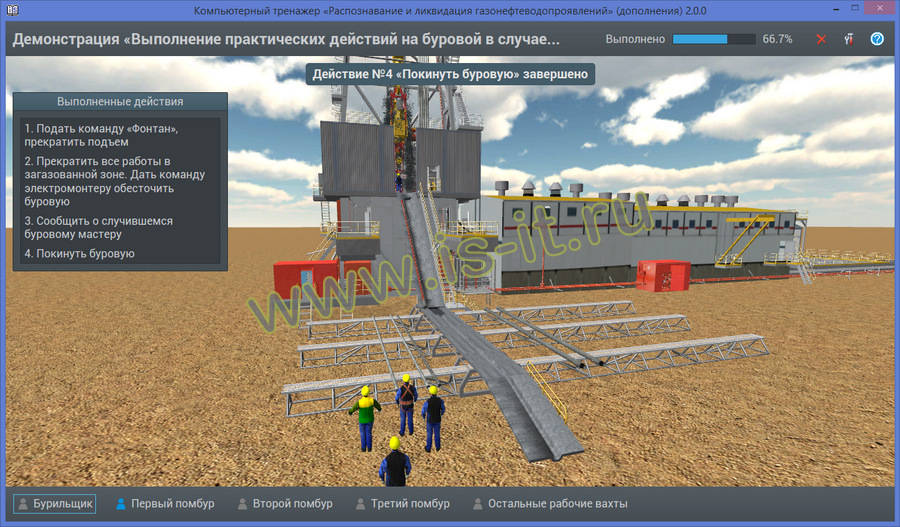
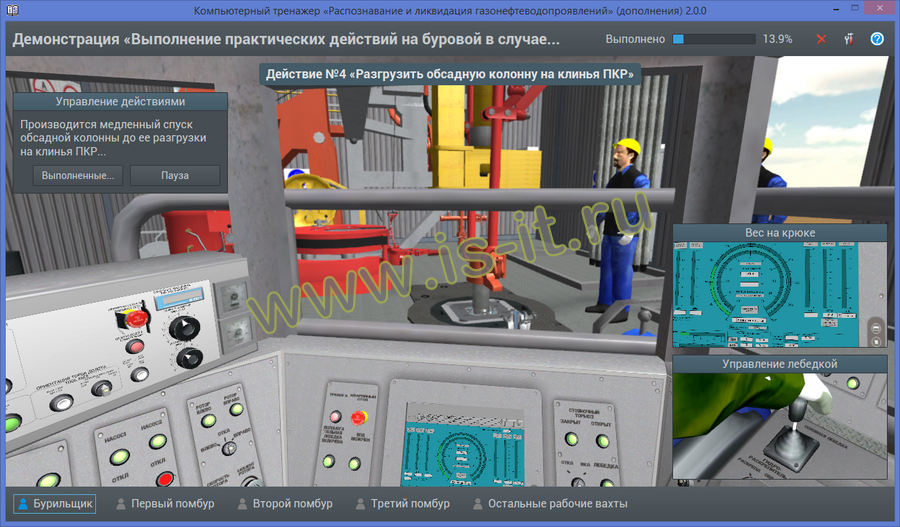
- Individual tasks concerning implementation of practical actions on the drilling rig as part of the plan of localization and liquidation of accidents:
- kick occur while drilling, reaming or washing the well,
- kick occur at round-trip,
- kick occur at setting the casing,
- kick if there are no drilling tools of casing in the well,
- wild flowing;
- Individual tasks concerning implementation of practical actions in the repair of wells as part of the plan of localization and liquidation of accidents:
- kick with smell of hydrogen sulfide at round-trip of oil-well tubing,
- kick occur at round-trip of electric rotary pump,
- kick occur at round-trip of sucker rod,
- kick if there are no oil-well tubing in the well,
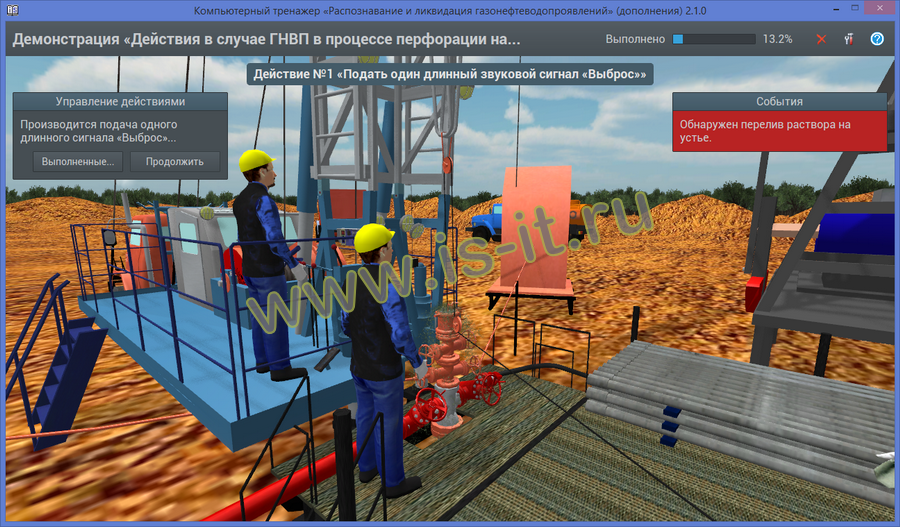
- kick occur in perforating process on logging cable.
Using the initial data a teacher can make his own tasks with various parameters (well, equipment and control parameters, etc.).
The result is delivered to the teacher’s WP in a form of detailed report, which contains charts, time lines, notifications, mistakes, and final evaluation. A trainee can also see his own result as a brief report delivered to his WP.
The simulator includes the electronic workbook “Well control during gas, oil, or water kicks”.

 (3412) 57-32-35
(3412) 57-32-35 office@is-it.ru
office@is-it.ru office_is
office_is